Gestational Diabetes: Ignoring sugar levels during pregnancy can be costly. Learn how to keep mother and child safe.
- bySherya
- 05 Jan, 2026
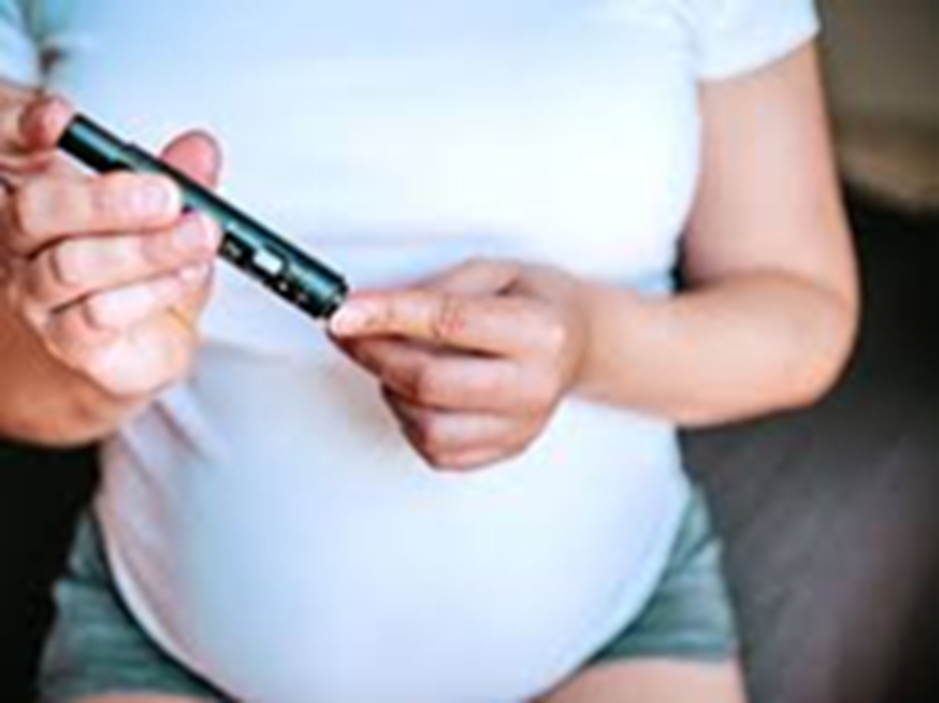

High Blood Sugar in Pregnancy: It's important to be mindful of many things during pregnancy. Let us explain how ignoring your blood sugar levels during pregnancy can be detrimental.

What is gestational diabetes?
How To Control Sugar During Pregnancy: Pregnancy is often considered a journey full of joy and excitement, but it can also pose some hidden health risks. One of these is gestational diabetes, which is now being recognized as a serious problem during pregnancy. In India, the guidelines of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of India, supported by the Ministry of Health, recommend screening of all pregnant women. The aim is to identify the disease early and reduce the risks to both mother and child.
What are its symptoms?
Gestational diabetes often progresses without any obvious symptoms, so many women remain undiagnosed until their blood sugar is high. If left untreated, it can lead to complications during delivery and increase the mother's risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. This is why timely diagnosis is crucial.
What do experts say?
According to health experts and the WHO, blood sugar testing should be done between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. However, DIPSI recommends starting testing even earlier, at the first antenatal visit, to help manage the disease early. Even if a woman doesn't have the usual risk factors for diabetes, screening helps detect the disease early. This allows timely measures such as dietary changes, blood sugar monitoring, and safe physical activity. According to DIPSI's 2023 guidelines, a simple non-fasting 75-gram glucose test is considered a cost-effective and reliable method that can be performed at primary health centers.
Its impact on children
If blood sugar levels are not controlled during pregnancy, they can affect the baby. High blood sugar can lead to excessive weight gain, which can cause complications during delivery. Some newborns may experience a sudden drop in blood sugar after birth, and in severe cases, they may need to be admitted to the NICU. Therefore, careful monitoring is essential throughout pregnancy. The main goal of managing gestational diabetes is to keep the mother's blood sugar levels stable. A balanced diet, which includes controlled carbohydrate intake and fiber-rich foods, is essential. Avoiding processed foods and excessively sweet foods helps prevent sudden spikes in blood sugar and improves the health of both mother and baby.
How can we protect ourselves?
Moderate exercise, such as daily walking or pregnancy-safe yoga, helps increase insulin sensitivity. If lifestyle changes alone don't control sugar, insulin or medications are prescribed under a doctor's supervision to protect both mother and fetus. The risk doesn't completely disappear even after delivery. Women who have had gestational diabetes are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes or prediabetes later in life. Therefore, blood sugar monitoring is considered essential within 4 to 12 weeks of delivery and then at regular intervals.