While most people are familiar with the need for vitamins and minerals in a balanced diet, there are certain nutrients that are often overlooked—glutamine being one of them. Glutamine is an amino acid crucial to various bodily functions, and although the body can produce it naturally, its demand can rise sharply under stress or illness.
What Is Glutamine?
Glutamine is a conditionally essential amino acid, meaning the body generally produces enough of it under normal conditions. It plays a key role in:
- Maintaining immunity
- Supporting gut health
- Building and repairing muscle tissues
- Promoting recovery after illness, surgery, or intense exercise
Dr. Ankit Bansal, Consultant in Internal Medicine and Infectious Diseases at Shri Balaji Action Medical Institute, Delhi, explains:
“Glutamine is vital for muscle strength, intestinal health, and immune response. In high-stress situations—whether due to mental pressure, infections, surgery, or strenuous workouts—glutamine levels can drop significantly, making supplementation or dietary support necessary.”
Signs of Glutamine Deficiency
A shortage of glutamine in the body can lead to:
- Persistent fatigue
- Muscle weakness
- Increased frequency of infections
- Digestive issues such as gas, bloating, or diarrhea
- Delayed recovery from wounds or injuries
- Unintended weight loss and a weakened immune system
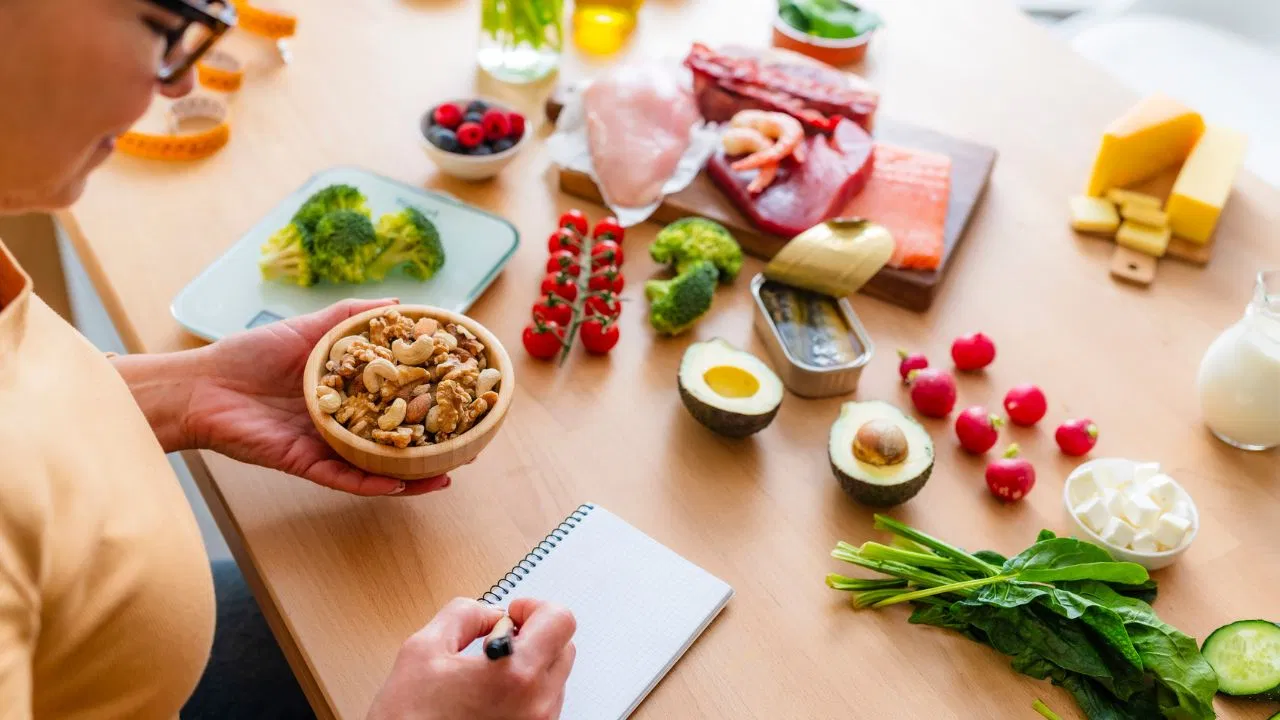
Dietary Sources of Glutamine
You can maintain healthy glutamine levels by consuming a balanced diet rich in:
- Eggs
- Chicken and fish
- Milk, curd, and cheese
- Pulses and legumes
- Nuts and seeds
- Green leafy vegetables
For athletes or individuals under physical stress, glutamine supplements may be recommended, but only under medical supervision. Self-supplementation without proper guidance could have unintended side effects.
Final Advice
If you’re experiencing symptoms like chronic fatigue, poor immunity, or slow recovery, consult a healthcare provider. A nutritional evaluation or test might be needed to assess glutamine levels. Fortunately, with a nutrient-rich diet, proper rest, and medical advice, glutamine deficiency can be managed effectively.